ExoCull is a procedural geometry-culling system designed to identify and remove non-contributing internal geometry from CAD-derived assemblies while preserving exterior appearance, part hierarchy, and downstream data integrity.
Before & After
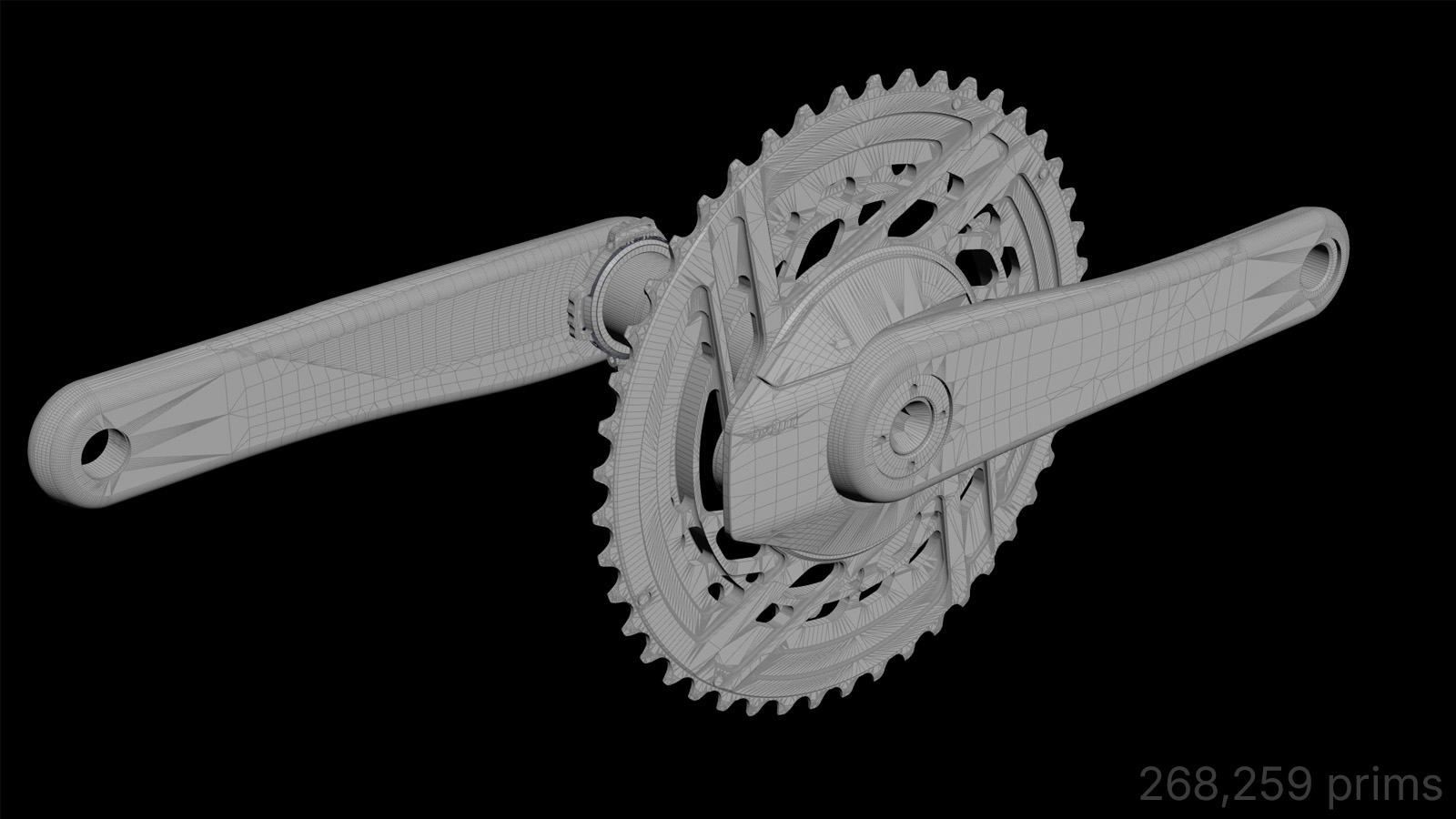
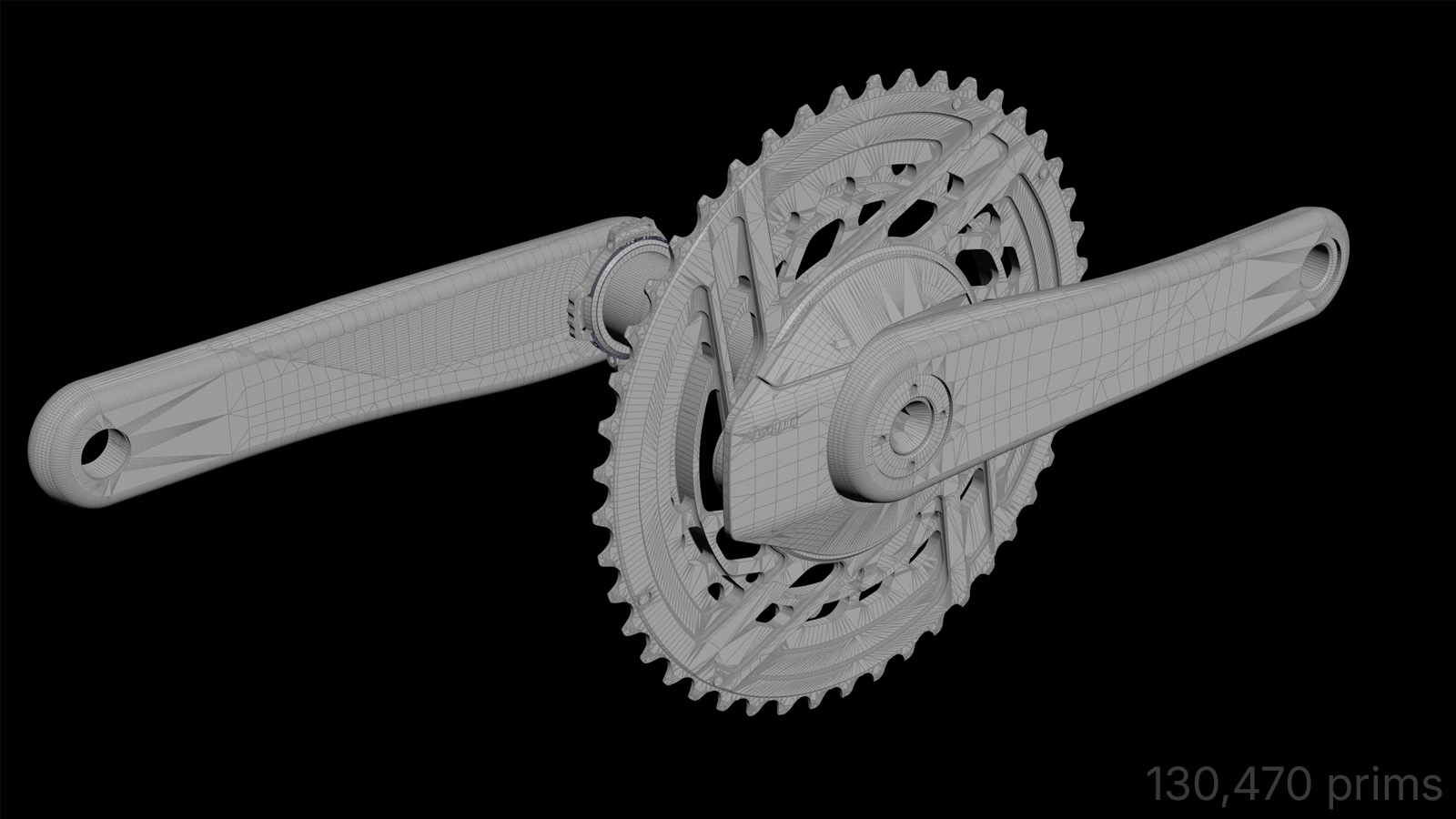
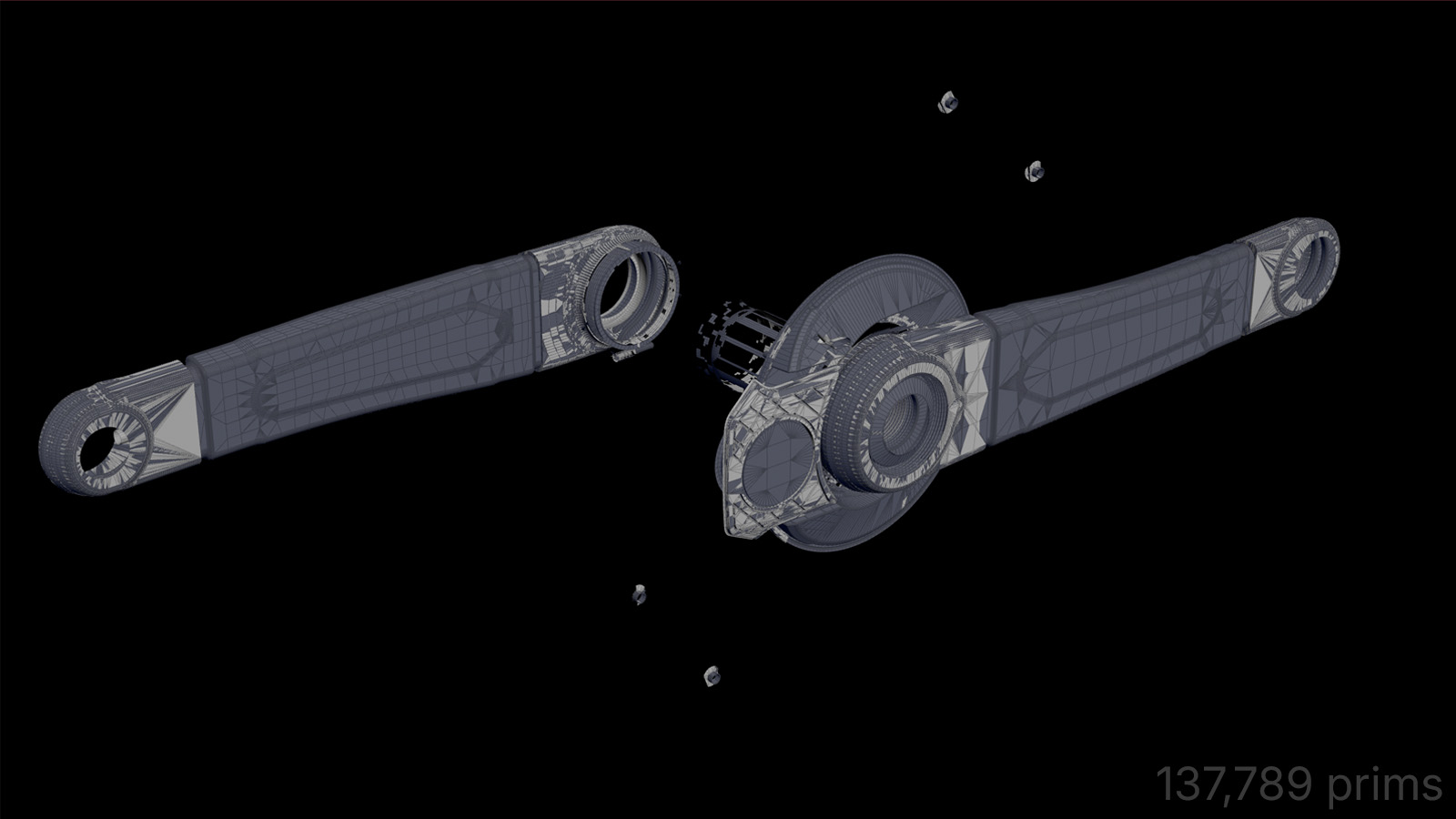
Removed Geometry
Problem
Engineering assemblies are authored for manufacturing, not downstream visualization or real-time use. As a result, they contain large amounts of internal geometry — fasteners, nested shells, overlapping volumes, and hidden cavities — that provide no external visual contribution.
- Long import and conversion times
- Excessive memory usage
- Unnecessary render complexity
- Poor performance in real-time engines
System strategy
ExoCull classifies geometry based on exterior reachability rather than volume or proximity. The goal is not geometric simplification, but deterministic identification of surfaces that meaningfully contribute to the external shell.
- Surface-level evaluation rather than volumetric booleans
- Deterministic, repeatable classification
- Attribute- and hierarchy-preserving operations
- Composable with downstream USD and real-time pipelines
How it works (implementation)
To classify exterior versus interior surfaces robustly across arbitrary CAD topology, ExoCull evaluates local surface exposure using a deterministic ray-casting strategy.
For each primitive face, a hemisphere of sample directions is generated, aligned to the face normal and originating from the face barycenter. Sample directions are distributed using a golden-ratio sequence to ensure even coverage without clustering artifacts.
Rays are cast outward along these directions and tested for intersection against surrounding geometry. Faces whose rays consistently escape without intersection are classified as externally visible; faces whose rays are occluded are flagged as internal and grouped for removal.
To handle cases where a face’s center is occluded but its perimeter remains externally visible, ExoCull performs a secondary evaluation using offset samples toward the face boundary before final classification.
This approach provides predictable behavior, avoids destructive topology operations, and scales efficiently across large assemblies.
Impact
- 40–70% reduction in polygon count, depending on assembly complexity
- Significantly faster asset ingestion into real-time environments
- Smaller USD / FBX / GLTF exports for downstream teams
- Cleaner geometry for shading, lighting, and material assignment
Technology & integration
Implemented as a Houdini-based procedural system integrated into a production CAD-to-USD pipeline. Designed for unattended, repeatable execution across large product libraries while preserving part identity and metadata for downstream consumers.